[理工学部、建築・環境学部教養学会ミニ講演会] (第66回理科系学生のための公開英語講演会)
Brain and Drug Addiction:
Brain Can Modulate Reward System
脳と薬物依存
講師: 理工学部、健康科学・テクノロジーコース
簑 弘幸 先生

In May 30th, 2024, the 66th session of the English Lecture Meeting for Science Major Students was held under the sponsorship of the Academic Society of Faculty of Liberal Arts, inviting Dr. Hiroyuki Mino of the College of Science and Technology to give a lecture with the above title, which was the 7th opportunity on which the lecturer gave a talk with the title to the audience consisting mainly of science major students.
Before starting the lecture, Dr. Mino made the following introductory remark: “I am Hiroyuki Mino from “Double E. Department” here at Kanto Gakuin University. The title of my talk today is “Brain and Drug Addiction – Drug Can Modulate Reward System.” As a matter of fact, I was worrying about having this title for this talk because we had a bitter experience several years ago, where some of our students were arrested on a charge of possession and intake of marijuana. However, I chose to give you my talk with this title because I wish all our students to know that taking drugs will have disastrous consequences for their health and life. So, let me remind you absolutely that you shouldn’t ever take drugs. If you ever happened to possess some drugs, you must trash it right away.”
The following shows a part of the introduction of this presentation:
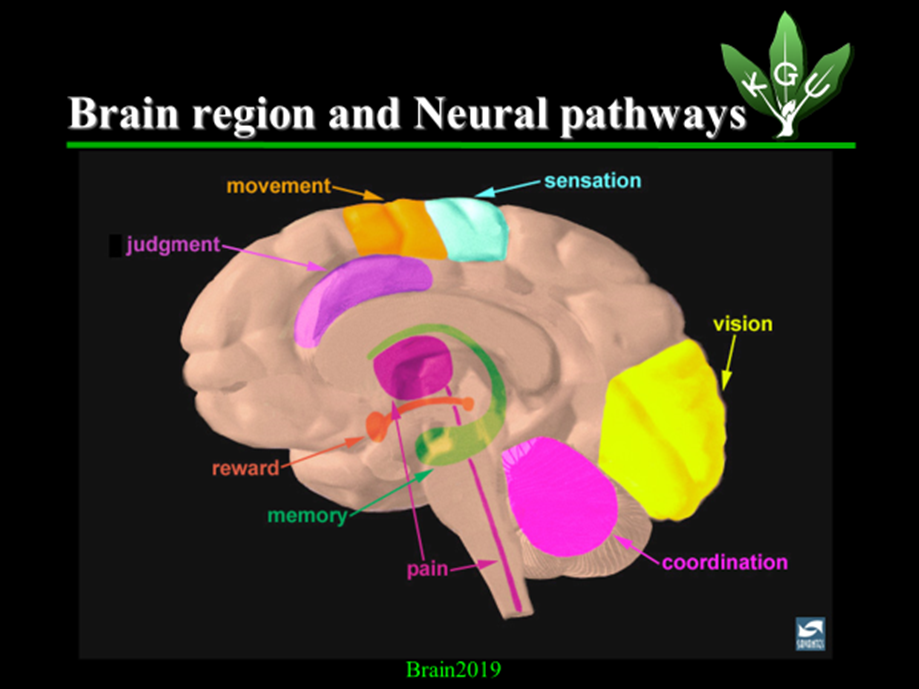
This is a picture of the brain cut down in the middle. The brain is divided into certain parts, and each of those parts has its own independent specific function. For example, the blue region is the area of somato-sensory system, the area governing our senses such as the sense of touch or tactile sensation. The orange region governs motor function or the function of movement, i.e. the function of sending a motor command to muscles. The yellow region is the area of visual cortex, which oversees our sense of sight. The relay station to each cortex, the magenta-colored region, is called “thalamus.” The green region is “hippocampus,” which governs memory function. The dark orange region in deeper brain is “nucleus accumbens,” in ventral striatum, projecting from ventral tegmental area (VTA).
As a focus of today’s talk, I would like you all to remember that the orange region called “reward pathway,” which stretches between the ventral tegmental area and the nucleus accumbens, is the reward system in the brain, in which your feeling of happiness or your sense of pleasure is created and controlled. Each region in the brain is constructed by nerve cells or neurons.
Now, take a closer look at the neurons and the neural pathways in the next slide:
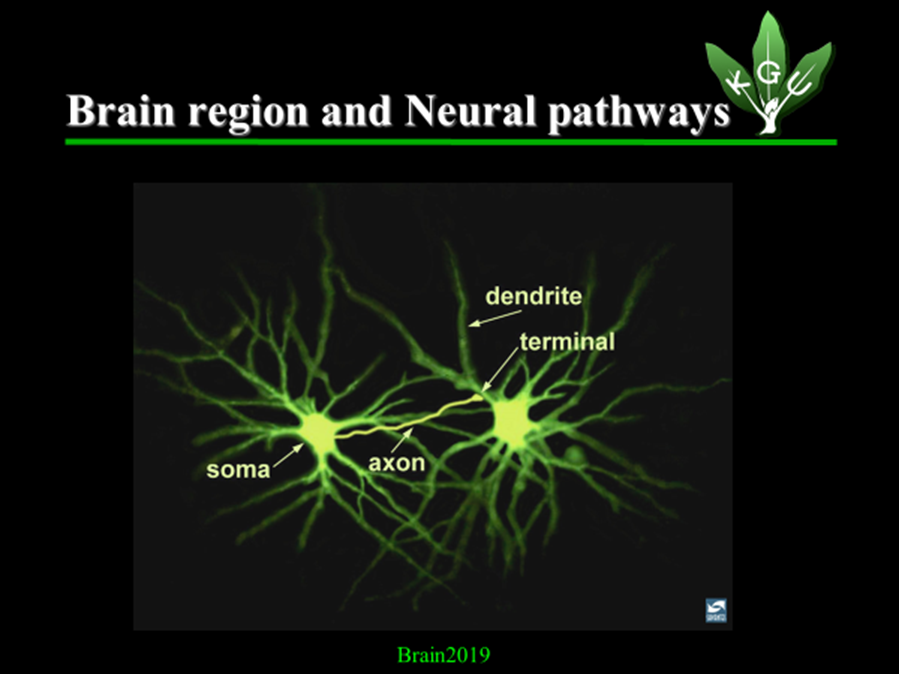
potential, which is an electrical signal; and the axon transmits the action potential to another neuron. The projection bridging the two neurons is called a “neural pathway.”
After having explained what harmful changes occur with the neural system of the brain when a person gets addicted to illegal drugs, Dr. Mino concluded his lecture with the following remarks, which seems to have fully convinced the audience of the disastrous consequence of taking illegal drugs: “You might wonder why some people cannot stop abusing illegal drugs even though those chemicals are obviously harmful to their health and their life, for that matter. The answer to your question is because addiction is truly a disease of the brain. I hope that now I have convincingly persuaded you that you must not dabble in drugs from the point of view of biomedical engineering. Thank you for your attention!”
In the second portion of this program, the Q and A session, nine questions were asked by the audience, to all of which Dr. Mino gave answers in detail, as represented by the following question and answer:
Q. I learned about harmful effects of drug abuse on the brain in my text. Professor Mino, is it possible to find ways to treat conditions such as drug addiction if we continue research in biomedical engineering?
私はテキストで薬物の使用による脳への影響について学びました。生体医工学の研究を続けることで薬物依存症などの症状を治療する方法を見つけることはできますか?
A. It’s a great question. Yes, I do believe so. We are trying to understand what’s gonna happen if deep brain stimulation is delivered to the patients of drug abuse, using neural network models through computer simulations. One of my master’s students sitting over there today, he’s gonna give a talk about this very topic in an international conference in the United States this coming July.







